刷题地址
题库 - 力扣 (LeetCode)
题解地址
CyC2018/CS-Notes
3.数组中重复的数字
把值为 i 的数值交换到 index 为 i 的位置上。(即实现了一个 hash)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
class Solution {
public:
void swap(int& a, int &b){
int t = a;
a = b;
b = t;
}
int findRepeatNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){
if(nums[i] == nums[nums[i]] && i != nums[i]){
//注意 i 不能等于 nums[i]
return nums[i];
}
else{
swap(nums[i], nums[nums[i]]);
if(nums[i] == nums[nums[i]] && i != nums[i]){
return nums[i];
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};
|
4.二维数组中的查找
从右上角开始查找,小的数在左,大的数在下。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
class Solution {
public:
bool findNumberIn2DArray(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {
if(matrix.size() == 0)return false; //注意边界
int i = 0, j = matrix[0].size() - 1;
while(i != matrix.size() && j != -1){
cout << matrix[i][j] << endl;
if(matrix[i][j] == target){
return true;
}
else if(matrix[i][j] > target){
j--;
}
else{
i++;
}
}
return false;
}
};
|
5.替换空格
把空格替换成%20:
先将数组补充到需要的长度,然后从后到前,使用快慢指针。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
class Solution {
public:
string replaceSpace(string s) {
string space = "%20";
int count = 0;
for(auto c : s){
if(c == ' '){
count++;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < count * 2; i++){
s += " ";
}
int i = s.size() - count*2 - 1;
int j = s.size() - 1;
for(; i >= 0; i--){
if(s[i] == ' '){
j -= 3;
s[j + 1] = '%', s[j + 2] = '2', s[j + 3] = '0';
}
else{
s[j--] = s[i];
}
}
return s;
}
};
|
6.从尾到头打印链表
方法一:递归 方法二:使用栈。两种方法的复杂度应该是一样的。
方法三:将链表倒置(头插法),再遍历。方法四:最后将结果转置。
7.重建二叉树
- 前序遍历:先遍历目前节点。
- 中序遍历:先遍历左子树,再遍历目前节点,最后遍历右子树。
- 后序遍历:先遍历左子树,再遍历右子树,最后遍历当前节点。
注意到 preorder 的第一个元素一定是 root,可以把 inorder 切割成两半,依次递归生成左子树和右子树。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
if(preorder.size() == 0 || inorder.size() == 0)return nullptr;
int rootval = -1;
int inorderRoot = -1;
for(rootval = 0; rootval < preorder.size(); rootval++){
auto it = find(inorder.begin(), inorder.end(), preorder[rootval]);
if(it != inorder.end()){
inorderRoot = distance(inorder.begin(), it);
break;
}
}
if(rootval == -1)return nullptr;
TreeNode * node = new TreeNode(preorder[rootval]);
vector<int> nextPreorder(preorder.begin() + rootval + 1, preorder.end());
vector<int> left(inorder.begin(), inorder.begin() + inorderRoot),
right(inorder.begin() + inorderRoot + 1, inorder.end());
node -> left = buildTree(nextPreorder, left);
node -> right = buildTree(nextPreorder, right);
return node;
}
};
|
这里还可以用for来做
9.两个栈实现队列
核心思想是,一个栈作为in的缓存区,一个栈作为out的缓存区。每次pop的时候,把in的元素全部push到out中。
注意在转移元素后还需要验证out是否为空。
10.1.斐波那契数列
可以用 dp 思想:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
class Solution {
public:
int fib(int n) {
int back = 0, front = 1, ans;
if(n == 0)return 0;
if(n == 1)return 1;
for(int i = 0; i <= n - 1; i++){
ans = (back + front) % 1000000007;
front = back;
back = ans;
}
return ans;
}
};
|
10.2.青蛙跳台阶
经典 dp 问题,首先是备忘录解法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
class Solution {
public:
int numWays(int n) {
if(n == 0)return 1;
vector<int> dp(n + 1, 0);
dp[0] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++){
dp[i] = dp[i] % 1000000007;
if(i < n)dp[i + 1] += dp[i];
if(i < n - 1)dp[i + 2] += dp[i];
}
return dp[n] % 1000000007;
}
};
|
其次是降维优化:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
class Solution {
public:
int numWays(int n) {
if(n == 0)return 1;
int front = 1, mid = 0, back = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
front = front % 1000000007;
if(i < n)mid += front;
if(i < n - 1)back += front;
front = mid;
mid = back;
back = 0;
}
return front % 1000000007;
}
};
|
11.旋转数组的最小数字
每次二分之后都会有一侧含有最小的数字。每次选择那一侧,右边界即为最小的数字。此外当检测到前指针的值等于后指针的值时,切换到顺序查找。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
class Solution {
public:
int minArray(vector<int>& nums) {
if (nums.size() == 0)
return 0;
int l = 0, h = nums.size() - 1;
while (l < h) {
int m = l + (h - l) / 2;
if (nums[l] == nums[m] && nums[m] == nums[h])
return minNumber(nums, l, h);
else if (nums[m] <= nums[h])
h = m;
else
l = m + 1;
}
return nums[l];
}
int minNumber(vector<int>& nums, int l, int h) {
for (int i = l; i < h; i++)
if (nums[i] > nums[i + 1])
return nums[i + 1];
return nums[l];
}
};
|
12.矩阵中的路径
回溯法直接开写:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
class Solution {
public:
bool exist(vector<vector<char>>& board, string word) {
for(int i = 0; i < board.size(); i++){
for(int j = 0; j < board[0].size(); j++){
if(backtrack(board, word, i, j, 0)){
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
private:
bool backtrack(vector<vector<char>>& board,
const string & word, int row, int col, int step){
char now = board[row][col];
if(now != word[step]){
return false;
}
else if(step + 1 == word.size()){
return true;
}//注意这里的终止条件判断
// cout << row << " " << col << " " << board[row][col] << endl;
board[row][col] = '\0';
if(row != 0 && board[row - 1][col] != '\0'){
if(backtrack(board, word, row - 1, col, step + 1)){
return true;
}
}
if(row != board.size() - 1 && board[row + 1][col] != '\0'){
if(backtrack(board, word, row + 1, col, step + 1)){
return true;
}
}
if(col != 0 && board[row][col - 1] != '\0'){
if(backtrack(board, word, row, col - 1, step + 1)){
return true;
}
}
if(col != board[0].size() - 1 && board[row][col + 1] != '\0'){
if(backtrack(board, word, row, col + 1, step + 1)){
return true;
}
}
board[row][col] = now;
return false;
}
};
|
13.机器人的运动范围
回溯法解决:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
class Solution {
public:
int movingCount(int m, int n, int k) {
int count = 0;
vector<bool> visted(m * n, false);
backtrack(k, 0, 0, m, n, visted);
for(int i = 0; i < m*n; i++){
if(visted[i])count++;
}
return count;
}
private:
bool check(int i, int j,int sum){
while(i != 0){
sum -= (i%10);
i /= 10;
}
while(j != 0){
sum -= (j%10);
j /= 10;
}
return (sum >= 0);
}
void backtrack(int k, int i, int j, int m, int n, vector<bool>& visted){
if(visted[i*n + j])return;
if(check(i, j, k)){
// cout << i << " " << j << endl;
visted[i*n + j] = true;
}
else{
return;
}
if(i != 0){
backtrack(k, i - 1, j, m, n, visted);
}
if(j != 0){
backtrack(k, i, j - 1, m, n, visted);
}
if(i != m - 1){
backtrack(k, i + 1, j, m, n, visted);
}
if(j != n - 1){
backtrack(k, i, j + 1, m, n, visted);
}
}
};
|
14.剪绳子
解法一:动态规划
解法二:当长度大于4时,优先剪长度为3的片段。
1
2
3
|
int cuttingRope(int n) {
return n <= 3? n - 1 : pow(3, n / 3) * 4 / (4 - n % 3);
}
|
big number版:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
class Solution {
public:
//n >= 5 2*(n-2) > n 3*(n-3) > n 且3*(n-3) >= 2*(n-2)
//n = 4 2 * 2 > 1 * 3
//2和3不能再分了 分了就变小了 且3优于2
int cuttingRope(int n) {
if (n <= 3) return n-1;
long rs = 1;
while (n > 4) {
//3最优
rs *= 3;
rs %= 1000000007;
n -= 3;
}
//循环结束 n只剩下1, 2 ,3,4
//1不能再分
//2,3再分会标小
//4 可以分成1 * 3 2 * 2,所以还是4最优
//所以 剩下的1 2 3 4 都不能再分了
return (rs * n) % 1000000007;
}
};
|
15. 二进制中1的个数
- 与运算
- 或运算
- 异或运算:两者不相同即为真
- 左移运算
- 右移运算
最简单的思路:当n不为0的时候,不断右移。
这里uint32_t代表这个是正数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
class Solution {
public:
int hammingWeight(uint32_t n) {
int count = 0;
while(n != 0){
count += (n%2);
n = n >> 1;
}
return count;
}
};
|
注意这里需要知道右移的效率比除以2的效率要高。且以上解法无法处理负数的case(右移会自动把第一位变成1)。
此外利用技巧n=n&(n-1) 可以直接减少1的位数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
class Solution {
public:
int hammingWeight(uint32_t n) {
int count = 0;
while(n){
n = n&(n-1);
count++;
}
return count;
}
};
|
负数的解决方法:
用一个flag变量作为掩码,避免死循环的问题。
16.数值的整数次方
虽然不需要考虑大数问题,但是需要考虑负数以及溢出问题。
此外利用了快速幂方法,降低复杂度。
$$x^n=\left{\begin{aligned}&x^{\frac{n}{2}}x^{\frac n2} \ (n \ even)\&x^{\frac{n-1}{2}}x^{\frac{n-1}{2}}x\ (n\ odd)\end{aligned}\right.$$
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
class Solution {
public:
double myPow(double x, int n) {
double result = 1.0;
if(n == 0){
return 1.0;
}
if(n == 1){
return x;
}
long nLong = n;
bool isNegative = (n < 0);
if(isNegative){
nLong = -nLong;
}
if(nLong % 2 == 0){
double sqrtResult = myPow(x, nLong / 2);
result = sqrtResult * sqrtResult;
}
else{
double sqrtResult = myPow(x, (nLong - 1) / 2);
result = sqrtResult * sqrtResult * x;
}
return isNegative? 1.0/result: result;
}
};
|
另外有位运算方法,如

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
class Solution {
public:
double myPow(double x, int n) {
double result = 1.0;
if(n == 0){
return 1.0;
}
if(n == 1){
return x;
}
long nLong = n;
bool isNegative = (n < 0);
if(isNegative){
nLong = -nLong;
}
while(nLong != 0){
if(nLong & 1){
result *= x;
}
x *= x;
nLong = nLong >> 1;
}
return isNegative? 1.0/result: result;
}
};
|
17.打印从1到n位最大的数
此题需要考虑大数问题。可以考虑为0-9的全排列,用回溯法直接解决。
或者在字符串上实现加法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
|
class Solution
{
public:
vector<int> res;
vector<int> printNumbers(int n) {
if (n <= 0) return res;
string number(n, '0');
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
//从高位到低位进行全排列
{
number[0] = i + '0';//首字符赋初值
permutationNumbers(number, n, 1);//设置下一位
}
return res;
}
//对数字全排列
void permutationNumbers(string& number, int length, int index) {
if (index == length) {//递归边界
saveNumber(number);//存储结果
return;
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
number[index] = '0' + i;//设置第index位的字符
permutationNumbers(number, length, index + 1);
}
}
}
//存储结果
//只能存储前导非0的排列
void saveNumber(string number) {
bool isBegin0 = true;
string tempStr = "";
string::iterator it = number.begin();
while (it != number.end())
{
if (isBegin0 && *it != '0') isBegin0 = false;
if (!isBegin0) {
tempStr += *it;
}
it++;
}
//从高位到低位全排列,要注意首字符为0时,tempStr为空,不能执行stoi
if (tempStr != "") {
int tempNum = stoi(tempStr);
res.push_back(tempNum);
}
}
};
|
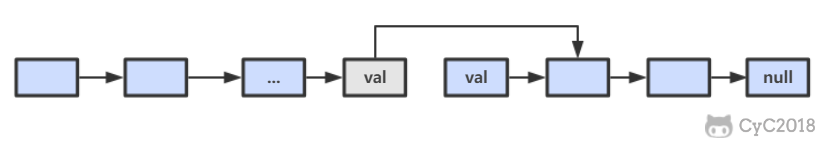
18.1 在 O(1) 时间内删除链表节点
假设已经知道要删除链表节点的地址,可以直接将该节点下一节点的值复制过来,再连接下下节点,最后删除下一个节点即可。
特性
- 当要删除的为最后一个节点,则需要换回顺序查找。
- 当删除节点为头节点的时候,需要返回nullptr
- 当节点数据非常大的时候,复制会非常久。
- 平均时间复杂度为O(1)。
- 需要编辑head的时候需要
ListNode**
这里传入的是指针的指针,但是由于→具有传递的性质,所以下面的行为与传入指针一样。同时又可以通过*p 编辑表头。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
void DeleteNode(ListNode** pListHead, ListNode* pToBeDeleted)
{
if(!pListHead || !pToBeDeleted)
return;
// 要删除的结点不是尾结点
if(pToBeDeleted->m_pNext != nullptr)
{
ListNode* pNext = pToBeDeleted->m_pNext;
pToBeDeleted->m_nValue = pNext->m_nValue;
pToBeDeleted->m_pNext = pNext->m_pNext;
delete pNext;
pNext = nullptr;
}
// 链表只有一个结点,删除头结点(也是尾结点)
else if(*pListHead == pToBeDeleted)
{
delete pToBeDeleted;
pToBeDeleted = nullptr;
*pListHead = nullptr;
}
// 链表中有多个结点,删除尾结点
else
{
ListNode* pNode = *pListHead;
while(pNode->m_pNext != pToBeDeleted)
{
pNode = pNode->m_pNext;
}
pNode->m_pNext = nullptr;
delete pToBeDeleted;
pToBeDeleted = nullptr;
}
}
|
19.正则表达式匹配
动态规划方法:
dp[i][j]代表前i个字符串是否能被前j个pattern匹配。
当pattern中为字母时:
$$dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-1]\cap s[i]==p[j]$$
当pattern中为.时:
$$dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-1]$$
以上两种情况应该写入一个match函数中。
当pattern 中为* :
若*没有被用上(*前面的字符匹配0次)
$$dp[i][j]=dp[i][j-2]$$
否则看最后一个字符是否匹配
$$dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j]\cup match(s[i],p[j-1])$$
Base:
$$dp[0][0]=true$$
注意这里是要(**m+1) X (n+1)**的dp数组的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
class Solution {
public:
bool isMatch(string s, string p) const {
int m = s.size(), n = p.size();
vector<vector<bool>> dp(m+1, vector<bool>(n+1, false));
dp[0][0] = true;
for(int i = 0; i <= m; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
// cout << i << " " << j << endl;
if(p[j-1] != '*'){
dp[i][j] = (i>0) && dp[i-1][j-1] && matches(s[i - 1], p[j - 1]);
}
else{
if(i != 0 && j > 1 && matches(s[i-1], p[j-1-1])){
dp[i][j] = ((j>0) && dp[i][j-1]) //singal a
|| (i>0&&dp[i-1][j]); //multiply a
}
if(j>=2)dp[i][j] = dp[i][j] || dp[i][j-2]; //zero a
}
// cout << "dp" << i << j << " " << dp[i][j] << endl;
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
private:
bool matches(char si, char pi) const{
return (pi == '.') || (pi == si);
}
};
|
简化版代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
public boolean match(char[] str, char[] pattern) {
int m = str.length, n = pattern.length;
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[m + 1][n + 1];
dp[0][0] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (pattern[i - 1] == '*')
dp[0][i] = dp[0][i - 2];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if (str[i - 1] == pattern[j - 1] || pattern[j - 1] == '.')
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
else if (pattern[j - 1] == '*')
if (pattern[j - 2] == str[i - 1] || pattern[j - 2] == '.') {
dp[i][j] |= dp[i][j - 1]; // a* counts as single a
dp[i][j] |= dp[i - 1][j]; // a* counts as multiple a
dp[i][j] |= dp[i][j - 2]; // a* counts as empty
} else
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 2]; // a* only counts as empty
return dp[m][n];
}
|
20.表示数值的字符串
有限状态自动机:
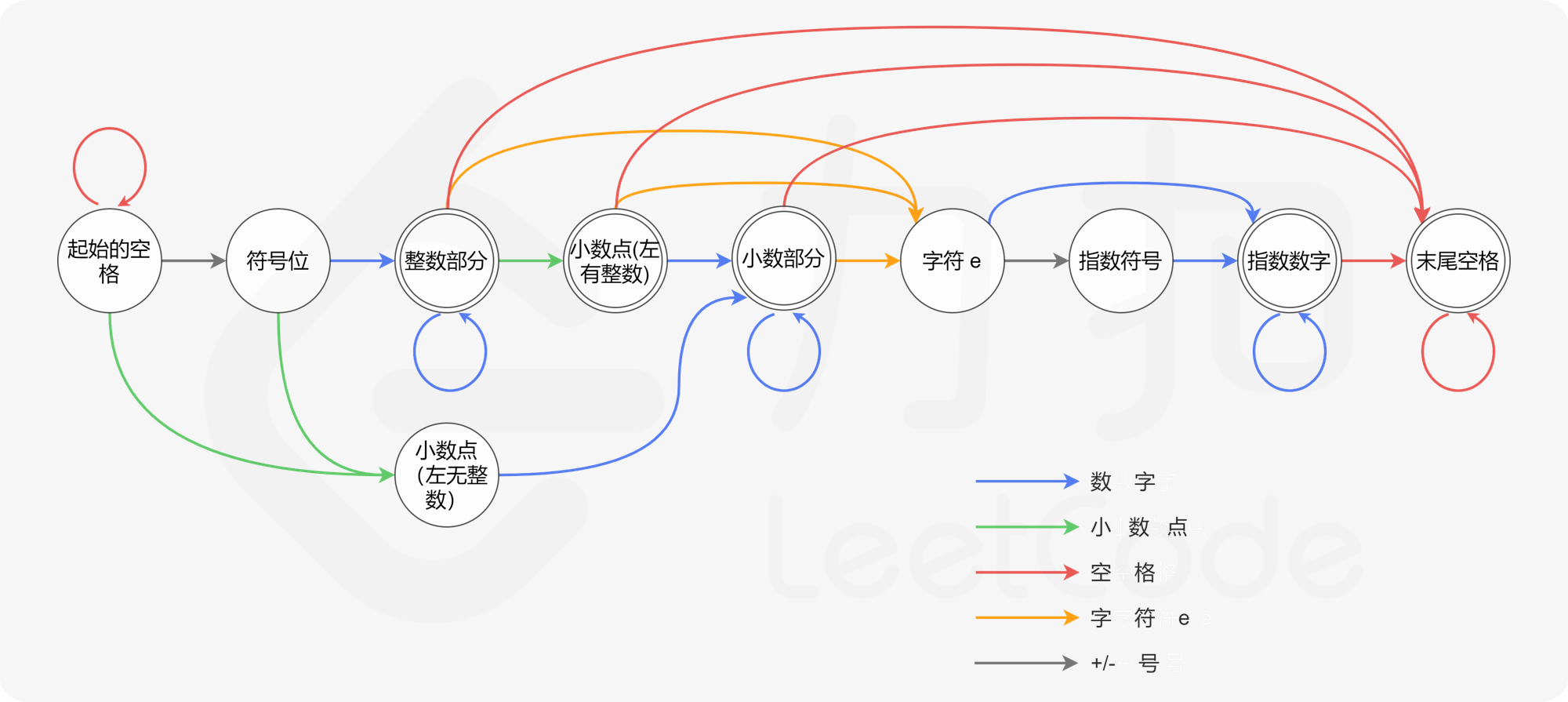
翻译成代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
|
class Solution {
public:
enum State {
STATE_INITIAL,
STATE_INT_SIGN,
STATE_INTEGER,
STATE_POINT,
STATE_POINT_WITHOUT_INT,
STATE_FRACTION,
STATE_EXP,
STATE_EXP_SIGN,
STATE_EXP_NUMBER,
STATE_END,
};
enum CharType {
CHAR_NUMBER,
CHAR_EXP,
CHAR_POINT,
CHAR_SIGN,
CHAR_SPACE,
CHAR_ILLEGAL,
};
CharType toCharType(char ch) {
if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
return CHAR_NUMBER;
} else if (ch == 'e' || ch == 'E') {
return CHAR_EXP;
} else if (ch == '.') {
return CHAR_POINT;
} else if (ch == '+' || ch == '-') {
return CHAR_SIGN;
} else if (ch == ' ') {
return CHAR_SPACE;
} else {
return CHAR_ILLEGAL;
}
}
bool isNumber(string s) {
unordered_map<State, unordered_map<CharType, State>> transfer{
{
STATE_INITIAL, {
{CHAR_SPACE, STATE_INITIAL},
{CHAR_NUMBER, STATE_INTEGER},
{CHAR_POINT, STATE_POINT_WITHOUT_INT},
{CHAR_SIGN, STATE_INT_SIGN},
}
}, {
STATE_INT_SIGN, {
{CHAR_NUMBER, STATE_INTEGER},
{CHAR_POINT, STATE_POINT_WITHOUT_INT},
}
}, {
STATE_INTEGER, {
{CHAR_NUMBER, STATE_INTEGER},
{CHAR_EXP, STATE_EXP},
{CHAR_POINT, STATE_POINT},
{CHAR_SPACE, STATE_END},
}
}, {
STATE_POINT, {
{CHAR_NUMBER, STATE_FRACTION},
{CHAR_EXP, STATE_EXP},
{CHAR_SPACE, STATE_END},
}
}, {
STATE_POINT_WITHOUT_INT, {
{CHAR_NUMBER, STATE_FRACTION},
}
}, {
STATE_FRACTION,
{
{CHAR_NUMBER, STATE_FRACTION},
{CHAR_EXP, STATE_EXP},
{CHAR_SPACE, STATE_END},
}
}, {
STATE_EXP,
{
{CHAR_NUMBER, STATE_EXP_NUMBER},
{CHAR_SIGN, STATE_EXP_SIGN},
}
}, {
STATE_EXP_SIGN, {
{CHAR_NUMBER, STATE_EXP_NUMBER},
}
}, {
STATE_EXP_NUMBER, {
{CHAR_NUMBER, STATE_EXP_NUMBER},
{CHAR_SPACE, STATE_END},
}
}, {
STATE_END, {
{CHAR_SPACE, STATE_END},
}
}
};
int len = s.length();
State st = STATE_INITIAL;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
CharType typ = toCharType(s[i]);
if (transfer[st].find(typ) == transfer[st].end()) {
return false;
} else {
st = transfer[st][typ];
}
}
return st == STATE_INTEGER || st == STATE_POINT || st == STATE_FRACTION || st == STATE_EXP_NUMBER || st == STATE_END;
}
};
|
21.调整数组顺序使得奇数在偶数前面
双指针:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> exchange(vector<int>& nums) {
int left = 0, right = nums.size() - 1;
while(left < right){
if(nums[left] % 2 == 1){
left++;
}
else if(nums[right] % 2 == 0){
right--;
}
else{
swap(nums[left], nums[right]);
left++;
right--;
}
}
return nums;
}
private:
void swap(int & a, int & b){
int t = a;
a = b;
b = t;
}
};
|
22.链表中倒数第 k 个节点
快慢指针,注意边界
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* getKthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int k) {
if(head == nullptr)return head;
ListNode* back = head;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
if(back -> next == nullptr){
return head;
}
back = back -> next;
}
while(back != nullptr){
back = back -> next;
head = head -> next;
}
return head;
}
};
|
23. 链表中环的入口结点
双指针法。fast 指针是 slow 指针速度的两倍。假设环入口节点为 y1,相遇所在节点为 z1。
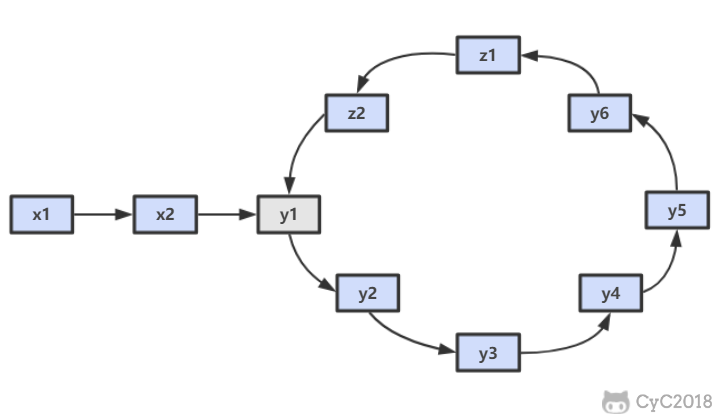
第一次相遇,此时 fast 走过$x+Ny+(N-1)z$。slow 走过$x+y$。同时又有$2(x+y)=x+Ny+(N-1)z$.解得$x=(N-2)y+(N-1)z=(N-2)C+z$.
这个等式左边是从起点x1 到环入口节点 y1 的长度,而右边是在圆环中走过 (N-2) 圈,再从相遇点 z1 再走过长度为 z 的长度。此时我们可以发现如果让两个指针同时从起点 x1 和相遇点 z1 开始,每次只走过一个距离,那么最后他们会在环入口节点相遇。
即 slow 走过:
$x+y+x=x+y+(N-2)y+(N-1)z=x+(N-1)C$
fast走过: $x$
两者相遇于入口。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode* pHead)
{
if(pHead == nullptr || pHead -> next == nullptr){
return nullptr;
}
ListNode* slow = pHead, * fast = pHead;
while(fast -> next != nullptr && fast -> next -> next != nullptr){
fast = fast -> next -> next;
slow = slow -> next;
if(slow == fast){
break;
}
}
fast = pHead;
while(fast != slow){
fast = fast -> next;
slow = slow -> next;
}
return fast;
}
};
|
24.反转链表
三个指针:head mid back
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)return head;
ListNode* mid = head -> next, *back = mid -> next;
head -> next = nullptr;
while(back != nullptr){
mid -> next = head;
head = mid;
mid = back;
back = back -> next;
}
mid -> next = head;
return mid;
}
};
|
25.合并两个排序链表
双指针迭代:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode* head = new ListNode(1);
ListNode* ret = head;
while (l1 != NULL && l2 != NULL) {
if (l1->val < l2->val) {
head->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
} else {
head->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
head = head->next;
}
head->next = l1 == NULL ? l2 : l1;
return ret->next;
}
};
|
递归:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
if (l1 == NULL) {
return l2;
}
if (l2 == NULL) {
return l1;
}
if (l1->val <= l2->val) {
l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next, l2);
return l1;
}
l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2->next);
return l2;
}
};
|
26.树的子结构
判断一棵树是否为另一棵树的一部分。

使用两个树的遍历函数解决:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
class Solution {
public:
bool isSubStructure(TreeNode* A, TreeNode* B) const {
if(B == nullptr || A == nullptr)return false;
return locateAt(A, B)
|| isSubStructure(A->left, B)
|| isSubStructure(A->right, B);
}
private:
bool locateAt(TreeNode* A, TreeNode* B) const {
if(B == nullptr)return true;
if(A == nullptr)return false;
if(A->val != B->val){
return false;
}
return locateAt(A->left, B->left) &&
locateAt(A->right, B->right);
}
};
|
27.反转二叉树
遍历一次树搞定:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* mirrorTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr)return nullptr;
TreeNode* temp = root -> left;
root -> left = root -> right;
root -> right = temp;
mirrorTree(root -> left);
mirrorTree(root -> right);
return root;
}
};
|
28.对称二叉树
比较左树的左子树是否与右树的右子树相同。。。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
class Solution {
public:
bool solve(TreeNode* r1, TreeNode* r2){
if (r1 == nullptr && r2 == nullptr)
return true;
else if(r1 == nullptr || r2 == nullptr)
return false;
if (r1->val != r2 -> val)
return false;
return solve(r1->left, r2->right) && solve(r1->right, r2->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr)return true;
return solve(root -> left, root -> right);
}
};
|
29.顺时针打印矩阵
设置四个变量,直接打印:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
vector<int> res;
if(matrix.size() == 0 || matrix[0].size() == 0)return res;
int lt = 0, rt = matrix[0].size() - 1;
int lb = matrix.size() - 1;
while(2 * lt < min(matrix.size(), matrix[0].size())){ //!!!
// cout << lt << " " << lb << " " << rt << endl;
for(int i = lt; i <= rt; ++i)res.push_back(matrix[lt][i]);
if(lt >= lb)return res; //!!!
for(int i = lt + 1; i <= lb; ++i)res.push_back(matrix[i][rt]);
if(lt >= rt)return res; //!!!
for(int i = rt - 1; i >= lt; --i)res.push_back(matrix[lb][i]);
for(int i = lb - 1; i > lt; --i)res.push_back(matrix[i][lt]);
lt++;
rt--;
lb--;
}
return res;
}
};
|
这里第一第二次的打印都是打满的。
或者可以用 visted[m][n]构造一个螺旋走的递归函数。(类似于回溯法),这种方法的空间复杂度为 $O(mn)$。
一个更好的做法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
vector<int> res;
int m = matrix.size();
if(m == 0) return res;
int n = matrix[0].size();
for(int k = 0; 2 * k < min(m, n); ++k) {
for(int j = k; j < n - k; ++j) {
res.push_back(matrix[k][j]);
}
for(int i = k + 1; i < m - k; ++i) {
res.push_back(matrix[i][n - k - 1]);
}
if(2 * k + 1 >= min(m, n))return res;
for(int j = n - k - 2; j >= k; --j) {
res.push_back(matrix[m - k - 1][j]);
}
for(int i = m - k - 2; i > k; --i) {
res.push_back(matrix[i][k]);
}
}
return res;
}
};
|
30.实现 O(1)的 minStack
使用两个 stack,一个 记录数据,一个记录最小值。
注意记录最小值的条件为小于等于。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
class MinStack {
public:
MinStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
if(sortedData.empty() || x <= sortedData.top()){
sortedData.push(x);
}
data.push(x);
}
void pop() {
if(data.empty()){
return;
}
else{
if(sortedData.top() == top()){
sortedData.pop();
}
data.pop();
}
}
int top() {
if(!data.empty())return data.top();
else return -1;
}
int min() {
if(!data.empty()) return sortedData.top();
else return -1;
}
private:
stack<int> data;
stack<int> sortedData;
};
|
用户错用调用函数的情况可以用 assert 来进行防御性编程。
31.栈的压入,弹出序列
使用一个栈,每 push 一个元素,都去根据 popped 序列尝试 pop 所有的元素。最后检测是否完成了整个 popped 队列。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
class Solution {
public:
bool validateStackSequences(vector<int>& pushed, vector<int>& popped) {
if(popped.size() == 0)return true;
if(pushed.size() == 0)return false;
stack<int> s;
int pPopped = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < pushed.size(); i++){
s.push(pushed[i]);
//注意防止 pPopped 越界
while(!s.empty() && pPopped < popped.size() &&s.top() == popped[pPopped]){
s.pop();
pPopped++;
}
}
return pPopped == popped.size();
}
};
|
32.树的层序遍历
普通遍历
使用队列:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result;
if(root == nullptr)return result;
queue<TreeNode*> s;
s.push(root);
while(!s.empty()){
root = s.front();
s.pop();
if(root != nullptr){
result.push_back(root->val);
s.push(root->left);
s.push(root->right);
}
}
return result;
}
};
|
分层遍历:
另外记录一个变量 deep
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
class Solution {
public:
void traverse(TreeNode* root, vector<vector<int>>& result, int deep){
if(root == nullptr)return;
// cout << result.size() << deep << endl;
if (result.size() <= deep)
result.push_back(vector<int>(0));
if(root -> left != nullptr)result[deep].push_back(root -> left -> val);
if(root -> right != nullptr)result[deep].push_back(root -> right -> val);
traverse(root -> left, result, deep+1);
traverse(root -> right, result, deep+1);
}
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
if (root == nullptr)
return result;
result.push_back(vector<int>(0));
result[0].push_back(root -> val);
traverse(root, result, 1);
result.pop_back();
return result;
}
};
|
非递归可以用 queue 来实现,使用 dfs 时,queue 的长度代表了层数。
之字形:
可以对偶数层直接倒序。
或者使用 bfs+queue,此时 queue 的大小代表每层元素的数量。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) return {};
vector<vector<int> > res;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
bool odd = true;
while(!q.empty())
{
int size = q.size(); //队列大小表示当前层数的元素个数
vector<int> level(size); //存放每一层的元素值
for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i) //逐个对该层元素进行处理
{
TreeNode *temp = q.front();
q.pop();
int index = odd? i : (size-1-i); //如果为奇数行则从后向前加入元素
level[index] = temp->val;
if(temp->left) q.push(temp->left);
if(temp->right) q.push(temp->right);
}
odd = !odd;
res.push_back(level); //将当层元素加入res中
}
return res;
}
};
|
33.检查是否为有效的二叉搜索树后序遍历序列
最后一个元素一定 为 root,递归写法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
class Solution {
public:
bool verifyPostorder(vector<int>& postorder) {
return solve(postorder, 0, postorder.size());
}
private:
bool solve(const vector<int>& postorder, int start, int end) {
if(end - start <= 1)return true;
int rootVal = postorder[end - 1];
// cout << rootVal << endl;
int rightHead = end - 1;
for(int i = start;i <= end - 2; i++){
if(postorder[i] > rootVal){
rightHead = i;
break;
}
}
for(int i = rightHead + 1;i <= end - 2; i++){
if(postorder[i] < rootVal)return false;
}
return solve(postorder, start, rightHead)
&& solve(postorder, rightHead, end - 1);
}
};
|
34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
直接遍历:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
vector<int> path;
if(root == nullptr)return result;
traverse(root, sum, path, result);
return result;
}
private:
void traverse(TreeNode* root, int sum, vector<int>& path, vector<vector<int>>& result){
if(root == nullptr)return;
sum -= root -> val;
path.push_back(root -> val);
if(root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr && sum == 0)
result.push_back(path);
traverse(root->left, sum, path, result);
traverse(root->right, sum, path, result);
path.pop_back();
}
};
|
35.复杂链表的复制
输入一个复杂链表(每个节点中有节点值,以及两个指针,一个指向下一个节点,另一个特殊指针指向任意一个节点),返回结果为复制后复杂链表的 head。
- 在原来的链表每个节点后面复制该节点
- 复制 random 指针
- 拆分链表
留意复制 random 时为 clone -> next -> random = clone -> random **-> next**;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if(head == nullptr)return nullptr;
Node* clone = head;
// copy
while(clone != nullptr){
Node* cloneNext = new Node(clone->val), *next = clone -> next;
cloneNext -> next = next;
clone -> next = cloneNext;
clone = next;
}
// copy random
clone = head;
while(clone != nullptr){
if(clone -> random != nullptr)
clone -> next -> random = clone -> random **-> next**;
clone = clone -> next -> next;
}
// divide
Node* cloneHead = head -> next;
clone = cloneHead;
while(clone -> next != nullptr){
head -> next = clone -> next;
clone -> next = clone -> next -> next;
head = head -> next;
clone = clone -> next;
}
head -> next = nullptr;
return cloneHead;
}
};
|
关键是将原来的链表节点和新的链表节点一一对应,这里是 next,使用哈希可以变成map[oldNode]→newNode.
36.二叉搜索树与双向链表
搜索二叉树转换为双向链表
留意到搜索二叉树的中序遍历即为排序结果
递归记录 pre 指针和 head 指针:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
class Solution {
public:
Node* treeToDoublyList(Node* root) {
if(root == nullptr)return nullptr;
Node* pre = nullptr, *head = nullptr;
traverse(head, pre, root);
head -> left = pre;
pre -> right = head;
return head;
}
private:
void traverse(Node*& head, Node*& pre, Node* root){
if(root == nullptr)return;
if(head == nullptr && root -> left == nullptr)
head = root;
if(root->left)
traverse(head, pre, root -> left);
if(pre != nullptr){
pre -> right = root;
root -> left = pre;
}
pre = root;
traverse(head, pre, root -> right);
return;
}
};
|
37.序列化二叉树
先序遍历,注意减少字符串的复制:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
class Codec {
public:
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
string start ="[", end = "]";
string trans = serializeTraverse(root);
return start.append(trans.substr(0, trans.size() - 1).append(end));
}
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
if(data.size() <= 2)return nullptr;
int pos = 1;
return deserializeTraverse(data, pos);
}
private:
string serializeTraverse(TreeNode* root){
if(root == nullptr)return "null,";
string result = to_string(root -> val);
string sign = ",";
result = (result.append(sign)).append(serializeTraverse(root->left));
result = result.append(serializeTraverse(root->right));
return result;
}
TreeNode* deserializeTraverse(string& data, int& pos){
if(pos >= data.size())return nullptr;
if(data.substr(pos, 4) == "null"){
pos += 5;
return nullptr;
}
int posend = pos;
while(data[posend] != ',' && data[posend] != ']')posend++;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(stoi(data.substr(pos, posend - pos)));
pos += posend - pos + 1;
root -> left = deserializeTraverse(data, pos);
root -> right = deserializeTraverse(data, pos);
return root;
}
};
|
38.字符串的排列
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> permutation(string s) {
vector<string> res;
dfs(s, res, 0);
return res;
}
void dfs(string &s, vector<string> &res, int depth)
{
if(depth >= s.size()-1)
{
res.push_back(s);
return ;
}
unordered_set<char> used; //局部set去重
for(int i = depth; i < s.size(); ++i)
{
if(used.find(s[i]) != used.end()) continue; //去重
used.insert(s[i]);
swap(s[depth],s[i]);
dfs(s, res, depth+1);
swap(s[depth],s[i]); //回溯撤销操作
}
}
};
|
分别以每个元素作为开头,将后面的元素作为参数传入下一层递归:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> permutation(string s) {
vector<string> res;
dfs(res,s,0);
return res;
}
void dfs(vector<string> &res,string &s,int pos){
if(pos == s.size())
res.push_back(s);
for(int i=pos;i<s.size();i++){
bool flag = true;
//s[pos] ~ s[i - 1] 为已经作为过开头的元素
for(int j = pos;j<i;j++)//字母相同时,等效,剪枝
if(s[j] == s[i])
flag = false;
if(flag){
swap(s[pos],s[i]);
dfs(res,s,pos+1);
swap(s[pos],s[i]);
}
}
}
};
|
39.数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
- 哈希表统计每个数字出现次数。时间复杂度和空间复杂度都是$O(n)$。
- 数组排序法。把数组排序后,中点一定是出现次数超过一半的数。时间复杂度为$O(n\log_2n)$,空间复杂度为$O(1)$。
- 摩尔投票法。考虑让所有人来投票,最后的投票结果即为超过一半的数。时间复杂度$O(n)$ ,空间复杂度$O(1)$。
- 票数统计为 0 票,假设众数为
nums[0] 。
- 当票数大于 0,假设的众数不变;当等于 0,假设众数变为
nums[i+1] 。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
class Solution {
public:
int majorityElement(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size() == 0)return -1;
int most = nums[0];
int count = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++){
// cout << most << " " << count << endl;
if(nums[i] == most)count++;
else count--;
if(count <= 0){
most = nums[i + 1];
i++;
count = 1;
}
}
return most;
}
};
|
40.数组的前 k 个最小的数
-
排序后取前 k 个数。时间复杂度$O(n\log_2n)$,空间复杂度$O(n\log_2n)$。
-
大小为 K 的最小堆
使用一个大根堆实时维护数组的前 k 个最小值。时间复杂度$O(n\log k)$ 空间复杂度 $O(k)$。
使用c++中的 priority_queue ,底层为大根堆。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getLeastNumbers(vector<int>& arr, int k) {
vector<int> vec;
if(k == 0)return vec;
priority_queue<int> heap;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
heap.push(arr[i]);
}
for(int i = k; i < arr.size(); i++){
if(arr[i] < heap.top()){
heap.pop();
heap.push(arr[i]);
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
vec.push_back( heap.top());
heap.pop();
}
return vec;
}
};
|
-
利用快排函数快速切分
注意熟读快速排序函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
//严蔚敏《数据结构》标准分割函数
Paritition1(int A[], int low, int high) {
int pivot = A[low];
while (low < high) {
while (low < high && A[high] >= pivot) {
--high;
}
A[low] = A[high];
while (low < high && A[low] <= pivot) {
++low;
}
A[high] = A[low];
}
A[low] = pivot;
return low;
}
|
若分割点>k,即需要对左边进行分划
若分割点<k,即需要对右边进行分割
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getLeastNumbers(vector<int>& arr, int k) {
vector<int> vec;
if(k == 0)return vec;
if(k >= arr.size())return arr;
int dividePos = -1;
int start = 0, end = arr.size() - 1;
while(dividePos != k){
dividePos = partition(start, end, arr);
if(dividePos < k)start = dividePos + 1;
else if(dividePos > k) end = dividePos - 1;
}
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
vec.push_back(arr[i]);
}
return vec;
}
private:
int partition(int l, int r, vector<int>& nums){
int pivot = nums[r];
int i = l - 1;
for (int j = l; j <= r - 1; ++j) {
if (nums[j] <= pivot) {
i = i + 1;
swap(nums[i], nums[j]);
}
}
swap(nums[i + 1], nums[r]);
return i + 1;
}
}
|
41.数据流中的中位数
设计一种数据结构,可以随时得到中位数
方法:大根堆+小根堆,各自记录一半的数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
class MedianFinder {
public:
MedianFinder() {
m = 0;
n = 0;
}
~MedianFinder(){
}
void addNum(int num) {
if(num < findMedian()){
small.push(num);
n++;
}else{
big.push(-num);
m++;
}
while(m != n && m != n + 1){
if(m > n){
AtoB(big, small);
m--, n++;
}
else{
AtoB(small, big);
n--, m++;
}
}
}
double findMedian() {
if(m+n == 0)return 0.0;
if((m+n) % 2 == 0)return (-big.top() + small.top()) / 2.0;
else return -big.top();
}
private:
void AtoB(priority_queue<int>& A, priority_queue<int>& B){
B.push(-A.top());
A.pop();
}
priority_queue<int> big, small;
int m, n;
};
|
42.连续子数组的最大和
动态规划,dp[i]为以 i 字母为尾的最大和。
$$dp[i]=\max {nums[i],\ dp[i-1]+nums[i]}$$
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
class Solution {
public:
int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size() == 0)return INT_MIN;
vector<int> dp(nums.size());
dp[0] = nums[0];
int maxSum = nums[0];
for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++){
dp[i] = max(nums[i], dp[i - 1] + nums[i]);
maxSum = max(dp[i], maxSum);
}
return maxSum;
}
};
|
可以降维压缩到
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
class Solution {
public:
int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size() == 0)return INT_MIN;
int preSum = nums[0];
int maxSum = nums[0];
for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++){
preSum = max(nums[i], preSum + nums[i]);
maxSum = max(preSum, maxSum);
}
return maxSum;
}
};
|
43.n个整数的十进制表示中1出现的次数
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
**int countDigitOne(int n) {
int ones = 0;
for (long long m = 1; m <= n; m *= 10)
ones += (n/m + 8) / 10 * m + (n/m % 10 == 1) * (n%m + 1);
return ones;
}**
|
4+ lines, O(log n), C++/Java/Python - LeetCode Discuss
44.数字序列中的某一位数字
一位数,两位数,三位数,四位数对应的个数是10, 90, 900, 9000
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
class Solution
{
public:
int findNthDigit(int n)
{
if (n < 10)
return n;
/*一位数,两位数,三位数,四位数对应的个数是10, 90, 900, 9000*/
int bit(1);
long long lev(10), temp(1), index(1);
/*累计现在的位数index*/
while (1)
{
temp += (lev / 10) * 9 * bit;
/*如果index大于n,结束*/
if (n - temp < 0)
break;
index = temp;
lev *= 10;
++bit;
}
/*求取当前的数是什么*/
int num = (n - index) / bit + (lev / 10);
/*要求是这个数的第几位*/
int xindex = (n - index) % bit;
/*顺序从高到低,所以反过来求要除以10^x*/
int div = pow(10, bit - xindex - 1);
/*返回该位*/
return (num / div) % 10;
}
};
|
45.把数组排成最小的数
优先让首位数字最小,自定义 compare 函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
class Solution {
public:
string minNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
string result = "";
if(nums.size() == 0)return result;
if(nums.size() == 1)return to_string(nums[0]);
vector<string> data;
for(auto item : nums)data.push_back(to_string(item));
sort(data.begin(), data.end(), compare);
for(auto item: data)result.append(item);
return result;
}
private:
**static** bool compare(const string& a, const string& b){
return a+b < b+a;
}
};
|
46.把数字翻译成字符串
给定一个数字,我们按照如下规则把它翻译为字符串:0 翻译成 “a” ,1 翻译成 “b”,……,11 翻译成 “l”,……,25 翻译成 “z”。一个数字可能有多个翻译。请编程实现一个函数,用来计算一个数字有多少种不同的翻译方法。
动态规划:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
class Solution {
public:
int translateNum(int num) {
string nums = to_string(num);
int count = nums.size();
vector<int> dp(count, 0);
dp[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++){
dp[i] += dp[i - 1];
if(nums[i - 1] == '1' || (nums[i - 1] == '2') && nums[i] <= '5')
dp[i] += i > 1? dp[i - 2]: 1;
}
return dp[nums.size() - 1];
}
};
|
降维:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
class Solution {
public:
int translateNum(int num) {
string nums = to_string(num);
int count = nums.size();
int dp0 = 1, dp1 = 1, dp2 = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++){
dp2 += dp1;
if(nums[i - 1] == '1'
|| (nums[i - 1] == '2') && nums[i] <= '5')
dp2 += (i > 1)? dp0: 1;
dp0 = dp1, dp1 = dp2, dp2 = 0;
}
return dp1;
}
};
|
47.礼物的最大价值
动态规划:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
class Solution {
public:
int maxValue(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
vector<vector<int>> dp(grid.size(), vector<int>(grid[0].size()));
dp[0][0] = grid[0][0];
for(int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++){
for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].size(); j++){
if(i == 0 && j == 0)continue;
if(i == 0)dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1] + grid[i][j];
else if(j == 0)dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + grid[i][j];
else dp[i][j] = grid[i][j] + max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
return dp[grid.size() - 1][grid[0].size() - 1];
}
};
|
48.最长不含重复字符的子字符串
滑动窗口+哈希
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
map<char, int> m;
int ret = 0, l = 0, r = 0;
while (r < s.size()) {
if (m.find(s[r]) != m.end()) {
**l = max(l, m[s[r]] + 1); //忽略以前发生的冲突**
}
m[s[r]] = r;
r++;
ret = max(r - l, ret);
}
return ret;
}
};
|
49.丑数
要维持一个 N 长的数组,和三个 index,每次选择下次要走哪个 index.
$$dp[i] = \min(dp[a]*2,dp[b]*3,dp[c]*5)$$
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
class Solution {
public:
int nthUglyNumber(int n) {
if (n <= 6)return n;
vector<int> dp(n);
dp[0] = 1;
int i2 = 0, i3 = 0, i5 = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
// cout << dp[i2] << " " << dp[i3] << " " << dp[i5] << endl;
dp[i] = min(dp[i2] * 2, min(dp[i3] * 3, dp[i5] * 5));
// cout << dp[i] << endl;
**if(dp[i] == dp[i2] * 2)i2++;
if(dp[i] == dp[i3] * 3)i3++;
if(dp[i] == dp[i5] * 5)i5++;
//注意这里不能重复计算路径 如2x3 vs 3x2**
}
return dp[n - 1];
}
};
|
50.第一个只出现一次的字符
unordered_map
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
class Solution {
public:
char firstUniqChar(string s) {
unordered_map<char, int> m;
for(auto item: s)m[item]++;
for(auto item: s)
if(m[item] == 1)return item;
return ' ';
}
};
|
C++中要实现有序哈希的话,需要额外储存 vector 保存 keys。
51. 数组中的逆序对
归并排序算法:在 merge 时,right 数组的元素与 left 数组中剩下的元素都为逆序组。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
|
class Solution {
public:
int reversePairs(vector<int>& nums) {
int len = nums.size();
if (len < 2) {
return 0; // 若不存在数对,直接 return 0
}
vector<int> helper(len);
return reversePairs(nums, 0, len - 1, helper);
}
private:
int reversePairs(vector<int>& nums, int left, int right, vector<int>& helper) {
if (left == right) {
return 0; // 递归终止条件是只剩一个元素了(即不存在数对了)
}
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2; // 此算式等同于 (left + right) / 2,是为了避免溢出
int leftPairs = reversePairs(nums, left, mid, helper); // 计算左半部分的逆序对
int rightPairs = reversePairs(nums, mid + 1, right, helper); // 计算右半部分的逆序对
if (nums[mid] <= nums[mid + 1]) {
// 此判断用于加速,即如果左右都已排好序,而且左边的最大值 <= 右边的最小值,
// 那么就不存在跨越左边和右边的逆序对了
return leftPairs + rightPairs;
}
int crossPairs = mergeAndCount(nums, left, mid, right, helper); // 计算跨越左边和右边的逆序对
return leftPairs + rightPairs + crossPairs;
}
int mergeAndCount(vector<int>& nums, int left, int mid, int right, vector<int>& helper) {
// 本函数的前提条件是:左半部分和右半部分都是已经按升序排好序了的
// 因为本函数是从左右部分都是只有一个元素的情况开始运行的(自底向上),所以是可以保证前提条件的
for (int i = left; i <= right; ++i) {
helper[i] = nums[i]; // 先填充 helper 辅助数组
}
int i = left, j = mid + 1; // i 和 j 分别是左半部分和右半部分的起点
int count = 0; // count 用来统计逆序对数量
for (int k = left; k <= right; ++k) {
if (i == mid + 1) {
// 假如 i 已经越过左边的边界,直接填充右半部分进 nums
nums[k] = helper[j];
++j;
} else if (j == right + 1) {
// 假如 j 已经越过右边的边界,直接填充左半部分进 nums
nums[k] = helper[i];
++i;
} else if (helper[i] <= helper[j]) { // 注意健壮的归并排序这里要是 <=
// 假如左边小于等于右边,那就不是逆序对,不用修改 count
nums[k] = helper[i];
++i;
} else {
// 假如左边大于右边,是逆序对,count += 当前左边 [i, mid] 的所有元素
// 因为假如左边是 [7,8],右边是[5,6],然后 i 指向 7,j 指向 5
// 那么 5 和 7、8 都构成了逆序对,也就是此时有两对新的逆序对
// 所以可以总结出规律:count += mid - i + 1
nums[k] = helper[j];
count += mid - i + 1;
++j;
}
}
return count;
}
};
//作者:superkakayong
//链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/shu-zu-zhong-de-ni-xu-dui-lcof/solution/zi-jie-ti-ku-jian-51-kun-nan-shu-zu-zhon-eipc/
//来源:力扣(LeetCode)
|
52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点
双指针法:两个指针分别走链 A,链 B 和链 B,链 A,相遇时即为第一个公共节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
ListNode* pa = headA, * pb = headB;
while(pa != pb){
pa = pa ? pa -> next : headB;
pb = pb ? pb -> next : headA;
}
return pa;
}
};
|
53-I.在排序数组中寻找数字
牢记二分法搜寻左右边界的模板(左闭右开):
左边界:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
int binarySearchLeft(int left, int right, vector<int>& nums, int target){
int mid;
while(left < right){
mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(nums[mid] == target){
right = mid;
}
else if(nums[mid] < target){
left = mid + 1;
}
else if(nums[mid] > target){
right = mid;
}
}
return left >= 0 && left < nums.size()
&& nums[left] == target ? left : -1;
}
|
右边界:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
int binarySearchRight(int left, int right, vector<int>& nums, int target){
int mid;
while(left < right){
mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(nums[mid] == target){
left = mid + 1;
}
else if(nums[mid] < target){
left = mid + 1;
}
else if(nums[mid] > target){
right = mid;
}
}
return left - 1;
}
|
算法代码呼之欲出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
class Solution {
public:
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
if(nums.size() == 0)return 0;
int leftIndex = binarySearchLeft(0, nums.size(), nums, target);
if(leftIndex == -1) return 0;
int rightIndex = binarySearchRight(0, nums.size(), nums, target);
return rightIndex - leftIndex + 1;
}
private:
int binarySearchLeft(int left, int right, vector<int>& nums, int target){
int mid;
while(left < right){
mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(nums[mid] == target){
right = mid;
}
else if(nums[mid] < target){
left = mid + 1;
}
else if(nums[mid] > target){
right = mid;
}
}
return left >= 0 && left < nums.size() && nums[left] == target ? left : -1;
}
int binarySearchRight(int left, int right, vector<int>& nums, int target){
int mid;
while(left < right){
mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(nums[mid] == target){
left = mid + 1;
}
else if(nums[mid] < target){
left = mid + 1;
}
else if(nums[mid] > target){
right = mid;
}
}
return left - 1;
}
};
|
53-II 0~n-1中缺失的数字
即二分搜索正确排列的数组的右边界右边的那个 index。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
class Solution {
public:
int missingNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int left = 0, right = nums.size(), mid;
while(left < right){
mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(nums[mid] == mid){
left = mid + 1;
}else{
right = mid;
}
}
return left; //不需要 left - 1
}
};
|
54. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点
二叉搜索树right,root,left 的遍历即为从大到小的遍历。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
class Solution {
public:
int kthLargest(TreeNode* root, int& k) {
int val = root -> val;
if(root -> right)val = kthLargest(root -> right, k);
if(k == 0)return val;
if(--k == 0)return root -> val;
if(root -> left)return kthLargest(root -> left, k);
return 0;
}
};
|
55 - I. 二叉树的深度
后序遍历方法:此树的深度 等于 左子树的深度 与 右子树的深度 中的 最大值 + 1 。
时间复杂度是$O(n)$。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr)return 0;
return max(maxDepth(root -> left) + 1,
maxDepth(root -> right) + 1);
}
};
|
55-II.平衡二叉树的判断
自顶向下方法,时间复杂度为$O(n\log n)$。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
class Solution {
public:
bool tranverse(TreeNode* root, int& height){
int left = 0, right = 0;
if(root -> left != nullptr){
left ++;
if(!tranverse(root -> left, left)){
return false;
}
}
if (root->right != nullptr)
{
right ++;
if (!tranverse(root->right, right))
{
return false;
}
}
height = height + max(left, right);
if(abs(left - right) > 1)return false;
else return true;
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr)return true;
int height;
return tranverse(root, height);
}
};
|
自底向上方法,时间复杂度为$O(n)$。利用上面的 maxdepth 函数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr)return 0;
return max(maxDepth(root -> left) + 1, maxDepth(root -> right) + 1);
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr)return true;
return abs(maxDepth(root -> left) - maxDepth(root -> right)) < 2 &&
isBalanced(root -> left) && isBalanced(root -> right);
}
};
|
56 - I. 数组中数字出现的次数
排序后单指针,时间复杂度不符合要求,为$O(N\log N)$。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> singleNumbers(vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
vector<int>result;
int i = 1;
for(; i < nums.size(); ){
// cout << nums[i - 1] << " " << nums[i] << endl;
if(nums[i] != nums[i - 1]){
result.push_back(nums[(i++) - 1]);
}else{
i += 2;
}
}
if(i == nums.size())result.push_back(nums[i - 1]);
return result;
}
};
|
利用异或交换律+二分
力扣
异或:
- 交换律:a ^ b ^ c <=> a ^ c ^ b
- 任何数于0异或为任何数 0 ^ n => n
- 相同的数异或为0: n ^ n => 0
把所有数字异或,得到一个数,这个数必定是两个只出现一次的数字异或得到的。异或规则是两个相应的bit位相同为0,不同为1。根据这个任意找一个为1的数位,根据这个数位为0和1分成两个数组,这样必定把两个结果数分开了,再分别异或就能得到结果。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> singleNumbers(vector<int>& nums) {
int exor = 0;
for (int i : nums) {
exor ^= i; // 求出两个独立数字的异或值
}
int first1 = 1;
while (!(first1 & exor)) {
first1 <<= 1; // 找到该异或值从右往左第一个 1 出现的位置
}
int a = 0, b = 0;
for (int i : nums) {
if (i & first1) {
a ^= i; // 如果 i 从右往左第一个 1 出现的位置与异或值一样
}
else {
b ^= i; // 如果 i 从右往左第一个 1 出现的位置与异或值不一样
}
}
return {a, b};
}
};
//作者:superkakayong
//链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/shu-zu-zhong-shu-zi-chu-xian-de-ci-shu-lcof/solution/zi-jie-ti-ku-jian-56-i-zhong-deng-shu-zu-rdni/
//来源:力扣(LeetCode)
//著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
|
56 - II. 数组中数字出现的次数 II
- 哈希表方法,过于简单
- sort 也很简单
- 位运算法
力扣
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> binary(32, 0); // 因为 int 最大到 2^31,所以二进制形式最大为 32 位
for (int i : nums) {
for (int j = 31; j >= 0; --j) {
// 将 nums 的所有元素转为二进制并加起来
binary[j] += i & 1;
i >>= 1;
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int j = 31; j >= 0; --j) {
// 哪一位不能被3整除,就说明目标数字的二进制在那一位是 1
if (binary[j] % 3 != 0) {
res += pow(2, (31 - j));
}
}
return res;
}
};
/*
作者:superkakayong
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/shu-zu-zhong-shu-zi-chu-xian-de-ci-shu-ii-lcof/solution/zi-jie-ti-ku-jian-56-ii-zhong-deng-shu-z-qbp1/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。*/
|
57. 和为s的两个数字
正确性证明:
力扣
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int i = 0, j = nums.size() - 1;
while(nums[i] + nums[j] != target){
if(target < nums[i] + nums[j])j--;
else i++;
}
return {nums[i], nums[j]};
}
};
|
57 - II. 和为s的连续正数序列
数学优化法:
- 可分为偶数i份:最小的数大于 0 && 可以以连续整数分为 i 份(即最小的数%i ==0)
- 可分为奇数i份:最小的数大于 0 && 可以平均分为 i 份,中间的为平均数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> findContinuousSequence(int target) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
for(int i = target / 2; i >= 2; i--){
if((target / i - i / 2 + 1 > 0 && i % 2 == 0 && (target - (i*(i-1)/2) ) % i == 0 )
|| (target / i - i / 2> 0 && i % 2 == 1 && target % i == 0) ){
vector<int> temp;
for(int j = (target / i) - i / 2 + (i % 2 == 0); j <= (target / i) + i / 2; j++){
temp.push_back(j);
}
result.push_back(temp);
}
}
return result;
}
};
|
58-I.反转单词顺序
注意空格的处理,指针+字符串拼接方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
class Solution {
public:
string reverseWords(string s) {
vector<string> resList;
for(int i = s.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--){
if(s[i] == ' ')continue;
// cout << "=> i = " << i << " s[i]: " << s[i] << endl;
int j = i;
while(j >= 0 && s[j] != ' ')j--;
if(j != i)resList.push_back(s.substr(j + 1, i - j));
i = j;
}
string result = "";
int flag = 0;
for(auto si: resList){
// cout << "\"" << si << "\" ";
if(flag == 1)result.append(" ");
result.append(si);
flag = 1;
}
return result;
}
};
|
58 - II. 左旋转字符串
- 直接分割为两部分,拼接
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
class Solution {
public:
string reverseLeftWords(string &s, int n) {
if(n >= s.size())return s;
string left = s.substr(0, n), right = s.substr(n, s.size() - n);
return right.append(left);
}
};
|
空间复杂度$O(s.size())$。
- 只保存$\min(k,s.size()-k)$大小的数组,降低空间复杂度:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
class Solution {
public:
string reverseLeftWords(string &s, int k) {
if(k >= s.size())return s;
if(k <= s.size() / 2){
string temp = s.substr(k, s.size() - k);
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
s[s.size() - k + i] = s[i];
}
for(int i = 0; i < s.size() - k; i++){
s[i] = temp[i];
}
}
else{
string temp = s.substr(0, k);
for(int i = 0; i < s.size() - k; i++){
s[i] = s[k + i];
}
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
s[s.size() - k + i] = temp[i];
}
}
return s;
}
};
|
- 先反转前 k 个字符,再反转后面的字符,最后整体反转。
空间复杂度$O(1)$,时间复杂度$O(n\log n)$。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
class Solution {
public:
string reverseLeftWords(string &s, int k) {
if(k >= s.size())return s;
reverse(s.begin(), s.begin() + k);
reverse(s.begin() + k, s.end());
reverse(s.begin(), s.end());
return s;
}
};
|
59-I.滑动窗口的最大值
窗口对应的数据结构为 双端队列 ,本题使用 单调双向队列 即可解决以上问题。
力扣
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
if(nums.size() == 0)return {};
deque<int> q;
vector<int> result;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){
if(q.empty()){
q.push_back(i);
}
else{
// 检查过期的元素
while(!q.empty() && q.front() <= i - k)q.pop_front();
// 删除前面无用的较小元素
while(!q.empty() && nums[q.front()] < nums[i])q.pop_front();
// 删除后面较小的元素,保证有序性
while(!q.empty() && nums[q.back()] < nums[i])q.pop_back();
q.push_back(i);
}
if(i >= k - 1)result.push_back(nums[q.front()]);
}
return result;
}
};
|
59 - II. 队列的最大值
利用上题的滑动窗口思想,用一个 deque记录 maxvalue 的情况:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
class MaxQueue {
public:
MaxQueue() {
}
int max_value() {
if(data.empty())return -1;
return maxQueue.front();
}
void push_back(int value) {
while(!maxQueue.empty() && maxQueue.front() < value)maxQueue.pop_front();
while(!maxQueue.empty() && maxQueue.back() < value)maxQueue.pop_back();
data.push(value);
maxQueue.push_back(value);
}
int pop_front() {
if(data.empty())return -1;
int val = data.front();
if(val == max_value()){
maxQueue.pop_front();
}
data.pop();
return val;
}
private:
queue<int> data;
deque<int> maxQueue;
};
|
60. n个骰子的点数
动态规划:把每投一个骰子作为一个阶段i,转移方程为
$$dp[i][sum]=\sum_{value_i=1}^6 dp[i-1][sum-value_i]$$
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<double> dicesProbability(int n) {
int maxPossible = 6*n;
vector<vector<double>> dp(n, vector<double>(maxPossible + 1, 0));
for(int i = 1; i <= 6; ++i){
dp[0][i] = 1;
}
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i){
for(int j = i + 1; j <= 6 * (i + 1); j++){
for(int z = 1; z <= 6; z++){
if(j - z > 0)dp[i][j] += dp[i - 1][j - z];
}
}
}
int all = pow(6, n);
vector<double> result(dp[n - 1].begin() + n, dp[n - 1].end());
for(auto & item: result)item /= all;
return result;
}
};
|
可以降维为两个数组:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<double> dicesProbability(int n) {
int maxPossible = 6*n;
vector<double> pre (maxPossible + 1, 0);
vector<double>* cur;
for(int i = 1; i <= 6; ++i){
pre[i] = 1;
}
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i){
cur = new vector<double>(maxPossible + 1, 0);
for(int j = i + 1; j <= 6 * (i + 1); j++){
for(int z = 1; z <= 6; z++){
if(j - z > 0)(*cur)[j] += pre[j - z];
}
}
pre = *cur;
delete cur;
}
int all = pow(6, n);
vector<double> result(pre.begin() + n, pre.end());
for(auto & item: result)item /= all;
return result;
}
};
|
61. 扑克牌中的顺子
滑动窗口,用数组存储某张牌是否出现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
class Solution {
public:
bool isStraight(vector<int>& nums) {
int jorkerCount = 0;
vector<bool> cards(13, false);
for(auto ni: nums){
if(ni == 0)jorkerCount++;
else cards[ni - 1] = true;
}
for(int i = 0; i < 9; ++i){
int straight = jorkerCount;
for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++){
straight += cards[i + j];
}
if(straight == 5)return true;
}
return false;
}
};
|
62. 圆圈中最后剩下的数字
约瑟夫环问题:
用$f(N,M)$代表 N 个人报数,报到 M 时去掉那个人, 最终胜利者的坐标。递推公式为
$$f(N,M)=(f(N-1,M)+M)%N$$
约瑟夫环–公式法(递推公式)_再难也要坚持-CSDN博客_约瑟夫环公式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
class Solution {
public:
int lastRemaining(int n, int m) {
int f = 0;
for (int i = 2; i != n + 1; ++i) {
f = (m + f) % i;
}
return f;
}
};
|
63.股票的最大利润
我们只需要遍历价格数组一遍,记录历史最低点,然后在每一天考虑这么一个问题:如果我是在历史最低点买进的,那么我今天卖出能赚多少钱?当考虑完所有天数之时,我们就得到了最好的答案。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int n = prices.size();
if(n == 0)return 0;
// i 天卖出能得到的最大利润
vector<int> dp(n);
dp[0] = -prices[0];
int result = 0;
int buyPrices = -prices[0];
for(int i = 1; i < prices.size(); i++){
buyPrices = max(buyPrices, -prices[i]);
dp[i] = buyPrices + prices[i];
result = max(result, dp[i]);
}
return result;
}
};
|
64.求 1+2+…+n
要求不能使用乘除法、for、while、if、else、switch、case等关键字及条件判断语句(A?B:C)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
class Solution {
public:
int sumNums(int n) {
int sum = n;
bool t = (n > 0 && (sum += sumNums(n - 1)) );
return sum;
}
};
|
利用了&&的短路规则,实际上也是一个 if 判断
官方题解:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
|
class Solution {
public:
int sumNums(int n) {
int ans = 0, A = n, B = n + 1;
(B & 1) && (ans += A);
A <<= 1;
B >>= 1;
(B & 1) && (ans += A);
A <<= 1;
B >>= 1;
(B & 1) && (ans += A);
A <<= 1;
B >>= 1;
(B & 1) && (ans += A);
A <<= 1;
B >>= 1;
(B & 1) && (ans += A);
A <<= 1;
B >>= 1;
(B & 1) && (ans += A);
A <<= 1;
B >>= 1;
(B & 1) && (ans += A);
A <<= 1;
B >>= 1;
(B & 1) && (ans += A);
A <<= 1;
B >>= 1;
(B & 1) && (ans += A);
A <<= 1;
B >>= 1;
(B & 1) && (ans += A);
A <<= 1;
B >>= 1;
(B & 1) && (ans += A);
A <<= 1;
B >>= 1;
(B & 1) && (ans += A);
A <<= 1;
B >>= 1;
(B & 1) && (ans += A);
A <<= 1;
B >>= 1;
(B & 1) && (ans += A);
A <<= 1;
B >>= 1;
return ans >> 1;
}
};
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/qiu-12n-lcof/solution/qiu-12n-by-leetcode-solution/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
|
65.不用加减乘除做加法
a ^ b 表示没有考虑进位的情况下两数的和,(a & b) « 1 就是进位。
递归会终止的原因是 (a & b) « 1 最右边会多一个 0,那么继续递归,进位最右边的 0 会慢慢增多,最后进位会变为 0,递归终止。
1
2
3
|
int add(int a, int b) {
return b == 0 ? a : add(a ^ b, (a & b) << 1);
}
|
66.构建乘积数组
一次遍历就可以完成。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> constructArr(vector<int>& a) {
if(a.size() == 0)return {};
vector<int> b(a.size(), 1);
int leftBase = 1, rightBase = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++){
b[i] *= leftBase;
leftBase *= a[i];
b[a.size() - i - 1] *= rightBase;
rightBase *= a[a.size() - i - 1];
}
return b;
}
};
|
67. 把字符串转换成整数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
class Solution {
public:
int strToInt(string str) {
long x=0;
int nsigned=0; //记录是否已经读取到符号 -1为加号 +1为减号
int numbered = 0 ; //记录是否已经读取过数字
char t;
for(int i=0;i<str.size();i++){
t=str[i];
if(t=='-' || t=='+'){
if(nsigned!=0||numbered==1)
break;
else{
if(t=='-')nsigned=1;
else nsigned=-1;
}
}
else if(t==' '&& numbered==0 && nsigned==0) continue;
else if((t<'0'||t>'9')){
if(numbered==1) break;
else return 0;
}
else{
x=10*x+t-'0';
if((nsigned != 1) && x>INT_MAX)return INT_MAX;
if((nsigned == 1) && -x<INT_MIN)return INT_MIN;
numbered = 1;
}
}
if(nsigned==1) x=-x; //跳出循环后若已经读取到减号,则取负数
return x;
}
};
|
68-I.二叉搜索树的最近共同祖先
利用好二叉搜索树的性质:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root == nullptr)return nullptr;
if(p -> val < root -> val && q -> val < root -> val)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root -> left, p, q);
else if(p -> val > root -> val && q -> val > root -> val)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root -> right, p, q);
else return root;
}
};
|
68-II.二叉树的最近共同祖先
递归,理清返回参数的情况:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root == nullptr)return nullptr;
if(p -> val == root -> val || q -> val == root -> val)return root;
TreeNode* left = lowestCommonAncestor(root -> left, p, q),
*right = lowestCommonAncestor(root -> right, p, q);
if(left && right)return root;
else return left? left: right;
}
};
|





